瀏覽量: 102
- 產(chǎn)品名稱: Research Grade Trastuzumab ( 曲妥珠單抗 )
- 產(chǎn)品貨號: CSD00686
- 貨期: 現(xiàn)貨
- 價格與訂購: 2480
- 數(shù)量:
庫存: 100
- 規(guī)格: 50μg
- 產(chǎn)品信息
- 如何訂購
貨號(Catalog No.)
CSD00686
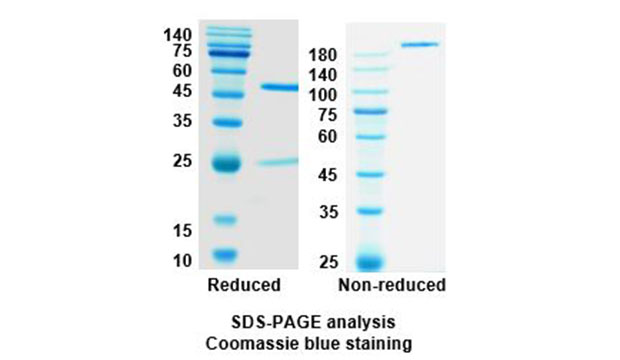
純度(Purity)
>95%
電泳圖(SDS-PAGE image)
濃度( Concentration)
1mg/ml
Formulation
PBS buffer PH7.5
Source
CHO cells
內(nèi)毒素(Endotoxin level)
Please contact with the lab for this information.
生物活性
產(chǎn)品描述(Description)
Trastuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody for patients with invasive breast cancers that overexpress HER2. Trastuzumab has the potential for HER2 Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer and HER2 Positive Gastric Cancer research.
靶點;物種(Specificity target name;species)
ERBB2 (HER2 ,Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2,MLN19,Metastatic lymph node gene 19 protein,ERBB2,Proto-oncogene Neu,p185erbB2,CD_antigen=CD340,Proto-oncogene c-ErbB-2,MLN 19,NEU,Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2,NGL) [Homo sapiens]
靶點背景信息(Target information)
Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor 2 (HER2) is also called ERBB2, HER-2,HER-2 /neu, NEU, NGL,TKR1 and c-erb B2,and is a protein giving higher aggressiveness in breast cancers. It is a member of the ErbB protein family, more commonly known as the epidermal growth factor receptor family. HER2 is a cell membrane surface-bound receptor tyrosine kinase and is normally involved in the signal transduction pathways leading to cell growth and differentiation. HER2 is thought to be an orphan receptor, with none of the EGF family of ligands able to activate it. Approximately 30% of breast cancers have an amplification of the HER2 gene or overexpression of its protein product. Overexpression of this receptor in breast cancer is associated with increased disease recurrence and worse prognosis. HER2 appears to play roles in development, cancer, communication at the neuromuscular junction and regulation of cell growth and differentiation .
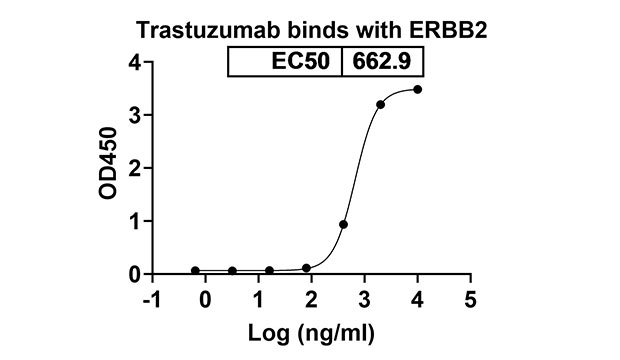
活性研究(體外/體內(nèi)研究)(Activity in vitro)
Treatment of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cell lines with Trastuzumab results in induction of p27KIP1 and the Rb-related protein, p130, which in turn significantly reduces the number of cells undergoing S-phase. A number of other phenotypic changes are observed in vitro as a consequence of Trastuzumab binding to HER2-overexpressing cells. Interaction of Trastuzumab with the human immune system via its human immunoglobulin G1 Fc domain may potentiate its antitumor activities. in vitro studies demonstrate that Trastuzumab is very effective in mediating antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against HER2-overexpressing tumor targets[1]. Trastuzumab consists of two antigen-specific sites that bind to the juxtamembrane portion of the extracellular domain of the HER2 receptor and that prevent the activation of its intracellular tyrosine kinase. Trastuzumab recruits immune effector cells that are responsible for antibody-dependent cytotoxicity[2]. The presence of Trastuzumab IgG significantly increases killing of all breast cancer cell lines. The ADCC activity of PBMCs evoked by Trastuzumab is equally strong against Trastuzumab-sensitive (SKBR-3) or Trastuzumab-resistant (JIMT-1) breast cancer cells, with dose-dependent cell death reaching 50–60% killing at an effector/target ratio of 60:1[3].
種類(Species)
Humanized
受體鑒定(Receptor identification)
Human IgG1
活性驗證(圖片、數(shù)據(jù))(Bioactivity)
化學(xué)信息
分子量(MV)
150000.00 Da
CAS
180288-69-1
存儲條件(Storage)
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Store at +4°C short term (1-2 weeks).
Store at -20 °C 12 months.
Store at -80°C long term.
Store at +4°C short term (1-2 weeks).
Store at -20 °C 12 months.
Store at -80°C long term.
參考文獻(xiàn)
1. Sliwkowski MX, et al. Nonclinical studies addressing the mechanism of action of trastuzumab. Semin Oncol. 1999 Aug;26(4 Suppl 12):60-70.
2. Hudis CA, et al. Trastuzumab--mechanism of action and use in clinical practice. N Engl J Med. 2007 Jul 5;357(1):39-51.
3. Barok M, et al. Trastuzumab causes antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-mediated growth inhibition of submacroscopic JIMT-1 breast cancer xenografts despite intrinsic drug resistance. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Jul;6(7):2065-72.
2. Hudis CA, et al. Trastuzumab--mechanism of action and use in clinical practice. N Engl J Med. 2007 Jul 5;357(1):39-51.
3. Barok M, et al. Trastuzumab causes antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-mediated growth inhibition of submacroscopic JIMT-1 breast cancer xenografts despite intrinsic drug resistance. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Jul;6(7):2065-72.
Note
For research use only .

 地 址:
地 址: 產(chǎn)品銷售:
產(chǎn)品銷售: E - mail :
E - mail : 郵 編:
郵 編:
 Amily
Amily